What is ixia-c
Ixia-c is a modern, powerful, and API-driven traffic generator designed to cater to the needs of hyperscalers, network hardware vendors, and hobbyists alike.
It is distributed and deployed as a multi-container application that consists of a controller, a traffic-engine, and an app-usage-reporter.
As a reference implementation of Open Traffic Generator API, Ixia-c supports client SDKs in various languages, most prevalent being snappi (Python SDK).
Keysight also offers a well supported commercial version, Keysight Elastic Network Generator, with no restrictions on performance and scalability. Scripts written for the free version are compatible with this version.
Quick Demo
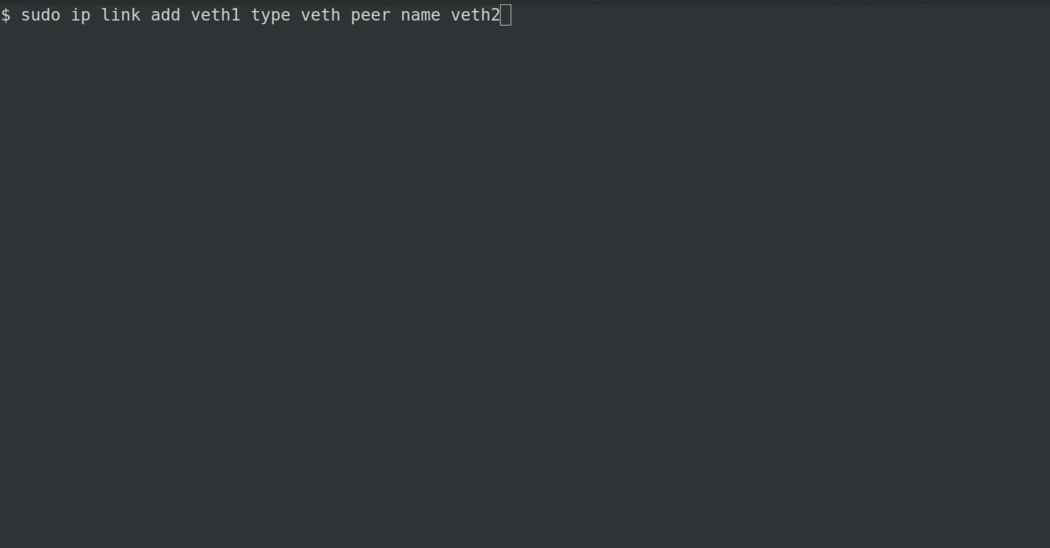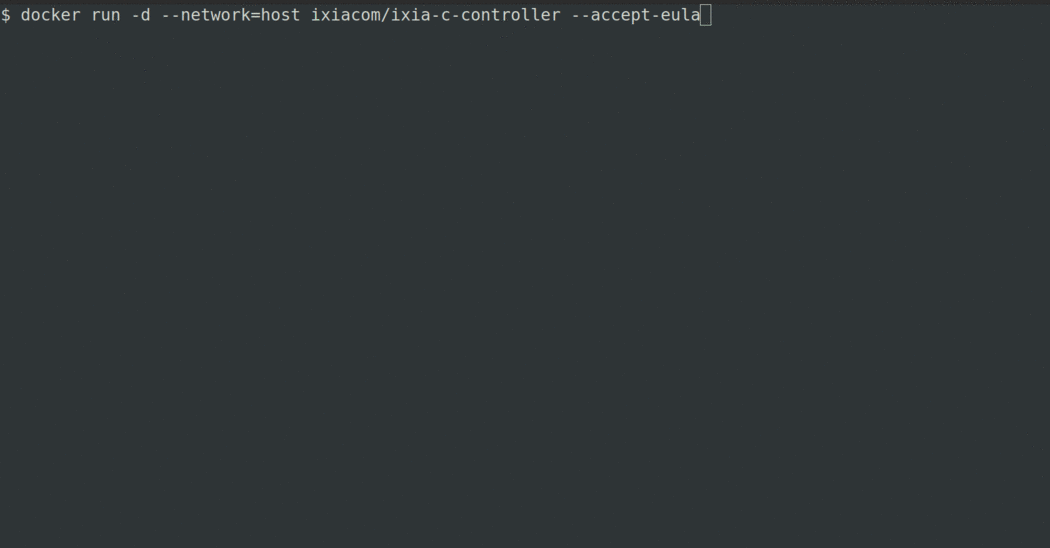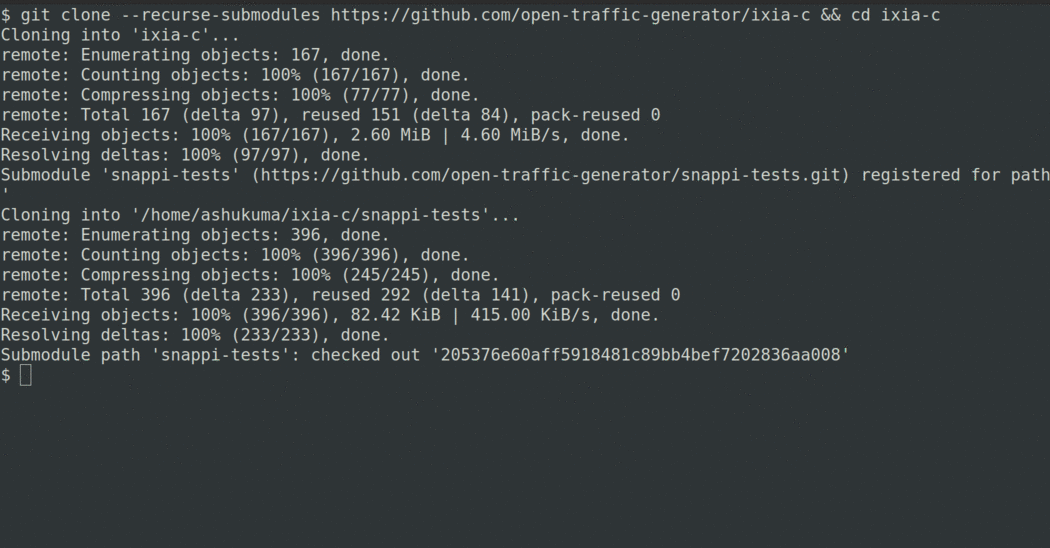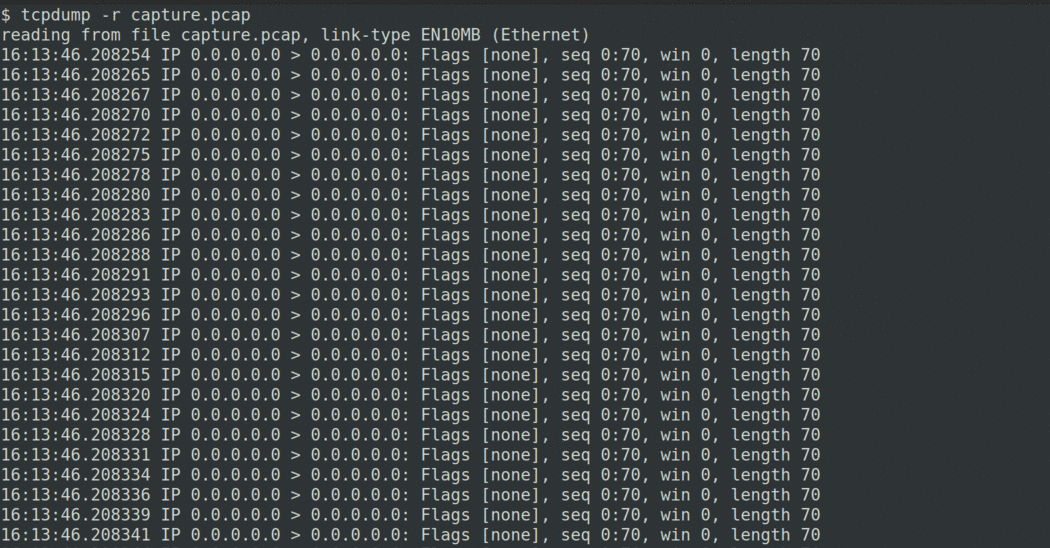
Quick Start
Before you proceed, ensure that the system prerequisites are met.
- Deploy Ixia-c
# start KENG controller
docker run -d --network=host ghcr.io/open-traffic-generator/keng-controller --accept-eula
docker run --net=host -d ghcr.io/open-traffic-generator/keng-app-usage-reporter
# start ixia-c traffic engine on eth1 interface
docker run -d --network=host --privileged \
-e ARG_IFACE_LIST="virtual@af_packet,eth1" \
-e OPT_NO_HUGEPAGES="Yes" \
ghcr.io/open-traffic-generator/ixia-c-traffic-engine
Once the containers are up, accessing https://controller-ip/docs/ will open up an interactive REST API documentation. For more information, see deployment guide.
- Generate Traffic using snappi. For more details on snappi, see hello-snappi.
# clone repo for test suites, useful helper scripts, deployment files, etc.
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/open-traffic-generator/ixia-c && cd ixia-c
# install snappi
python -m pip install --upgrade snappi==0.9.4
# run a standalone script to generate TCP traffic and fetch metrics
python snappi-tests/scripts/quickstart_snappi.py
After a successful run, the port metrics will be printed on the console.
Expand this section for an overview of the script you just ran
import snappi
# create a new API instance over HTTPS transport where location points to controller
api = snappi.api(location="https://localhost", verify=False)
# OR
# create a new API instance over gRPC transport where location points to controller
api = snappi.api(location="localhost:40051", transport=snappi.Transport.GRPC)
# create a config object to be pushed to controller
config = api.config()
# add a port with location pointing to traffic engine
prt = config.ports.port(name='prt', location='localhost:5555')[-1]
# add a flow and assign endpoints
flw = config.flows.flow(name='flw')[-1]
flw.tx_rx.port.tx_name = prt.name
# configure 100 packets to be sent, each having a size of 128 bytes
flw.size.fixed = 128
flw.duration.fixed_packets.packets = 100
# add Ethernet, IP and TCP protocol headers with defaults
flw.packet.ethernet().ipv4().tcp()
# push configuration
api.set_config(config)
# start transmitting configured flows
ts = api.transmit_state()
ts.state = ts.START
api.set_transmit_state(ts)
# fetch & print port metrics
req = api.metrics_request()
req.port.port_names = [prt.name]
print(api.get_metrics(req))
- Optionally, you can generate the traffic by using curl.
You can also pass an equivalent JSON configuration directly to the KENG controller by using curl and without installing snappi. For the detailed description of each node (and their attributes) in the JSON configuration, see Open Traffic Generator API.
# push the contents of config file snappi-tests/configs/quickstart_snappi.json
curl -k https://localhost/config -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @snappi-tests/configs/quickstart_snappi.json
# start transmitting configured flows
curl -k https://localhost/control/transmit -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"state": "start"}'
# fetch all port metrics
curl -k https://localhost/results/metrics -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"choice": "port"}}'